GRAD: Graph-Retrieved Adaptive Decoding for Hallucination Mitigation
PositiveArtificial Intelligence
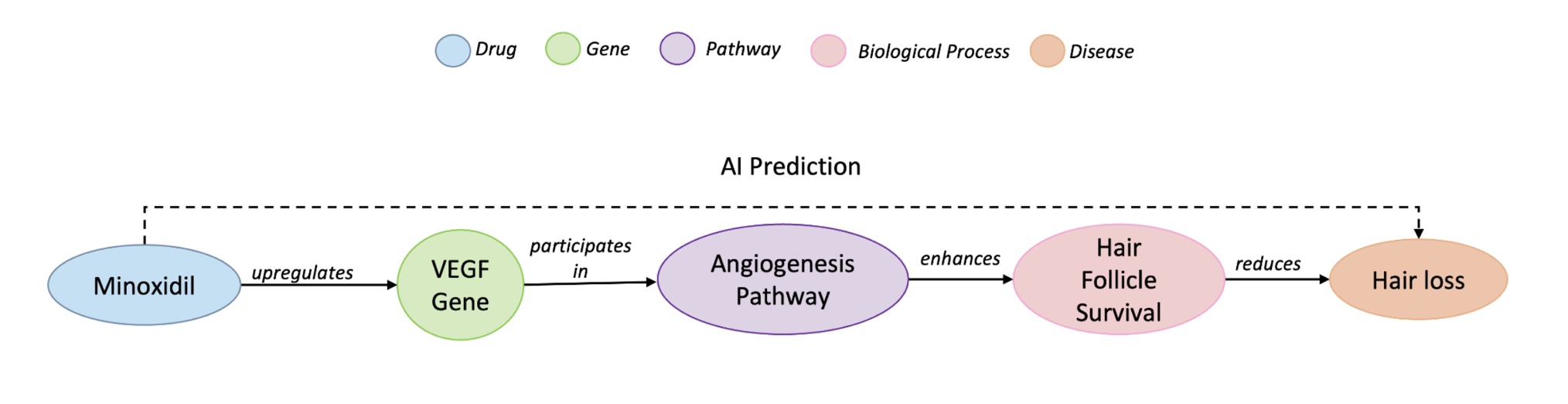
GRAD: Graph-Retrieved Adaptive Decoding for Hallucination Mitigation
A recent study introduces GRAD, a novel approach to mitigate hallucinations in large language models (LLMs). This method addresses the persistent challenge of inaccuracies in LLM outputs by leveraging knowledge graphs for more reliable information retrieval. Unlike traditional methods that can be fragile or costly, GRAD aims to enhance the robustness of LLMs, making them more effective for various applications. This advancement is significant as it could lead to more trustworthy AI systems, ultimately benefiting industries that rely on accurate language processing.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System