Layer-Wise High-Impact Parameter Ratio Optimization in Post-Training Quantization for Large Language Models
PositiveArtificial Intelligence
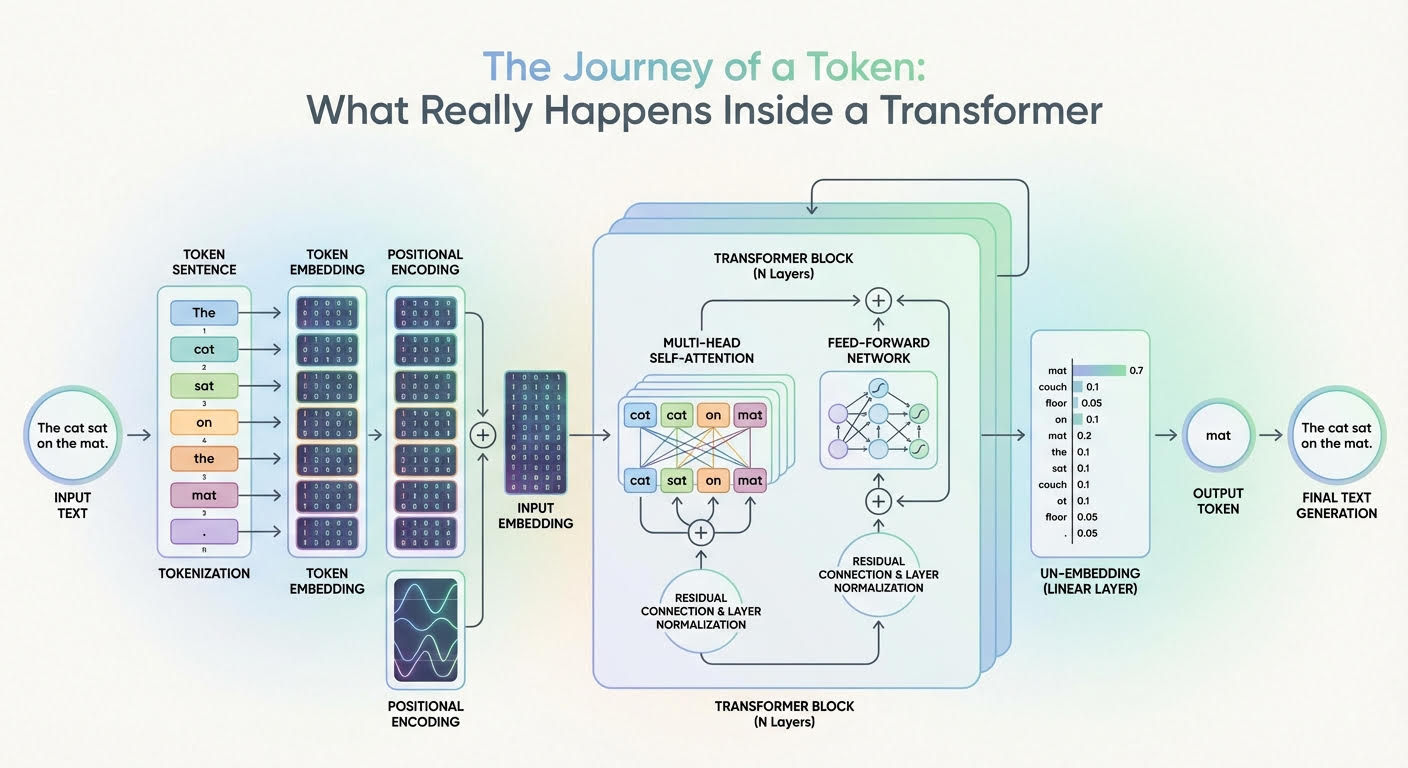
- A new study proposes a quadratic optimization framework for layer-wise high-impact parameter ratio optimization in post-training quantization (PTQ) for large language models (LLMs). This approach aims to enhance quantization performance by identifying and retaining high-impact parameters specific to each layer, addressing the significant accuracy loss typically encountered at low bit-widths.
- This development is crucial as it allows for more efficient deployment of LLMs, reducing computational and memory challenges while maintaining accuracy. By optimizing parameter ratios, the framework could lead to improved performance in various natural language processing applications.
- The advancement highlights ongoing challenges in the field of LLMs, such as label length bias and the need for reliable calibration methods to enhance trustworthiness. As researchers continue to explore ways to mitigate issues like hallucinations and over-refusal in LLM outputs, this optimization framework represents a significant step towards more robust and efficient AI models.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System