Teen turns his suburban home into elaborate haunted house every October
PositiveScience
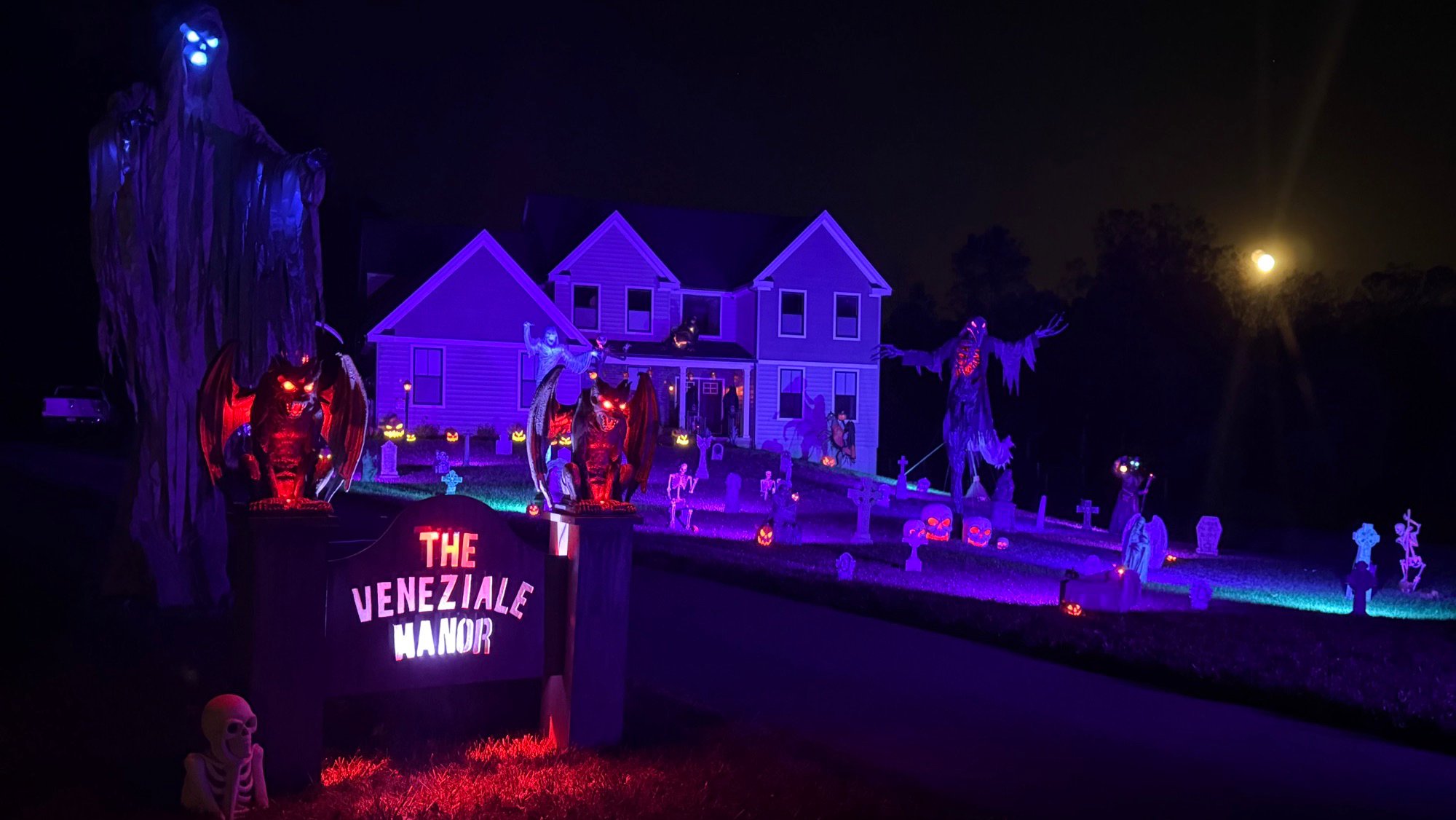

Every October, 16-year-old Joe Veneziale transforms his suburban home into an elaborate haunted house, and this year he has outdone himself with a terrifying Old Hollywood hotel theme. This creative endeavor not only showcases his impressive skills in design and construction but also brings joy and excitement to his community, making Halloween a memorable experience for everyone involved.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System