Cosmic 'brain' ponders the cosmos in colorful new photo of the Medulla Nebula
PositiveScience
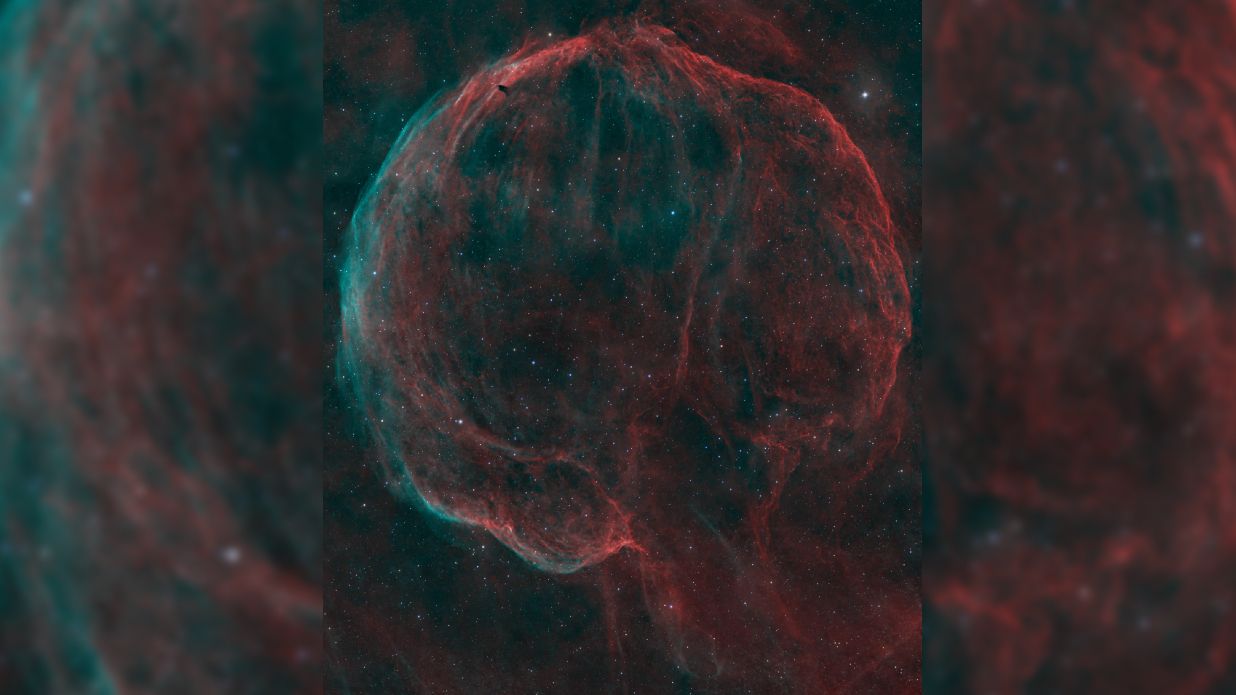

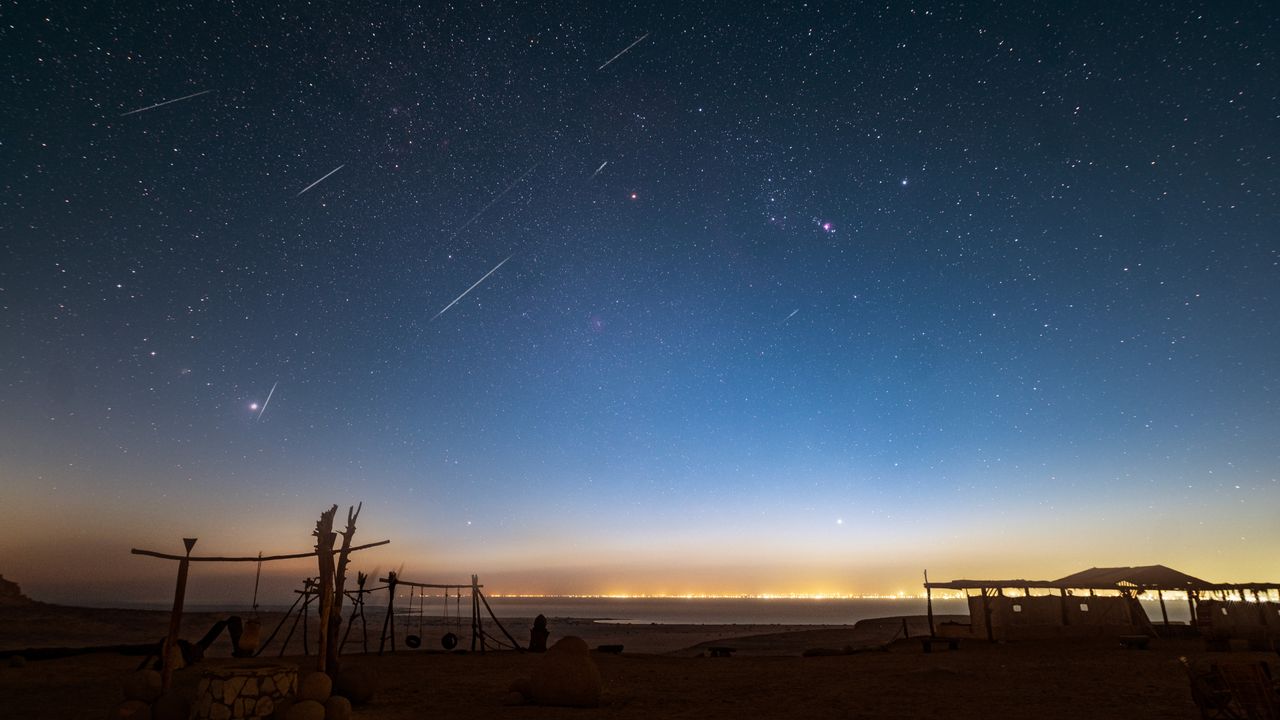
A stunning new photo of the Medulla Nebula, captured over 50 hours in September 2025, showcases the vibrant light from this ancient supernova remnant. This remarkable image not only highlights the beauty of the cosmos but also enhances our understanding of stellar evolution and the life cycle of stars. Such discoveries inspire curiosity and deepen our connection to the universe.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System