Interstellar object 3I/ATLAS is about to get very active — Space photo of the week
NeutralScience
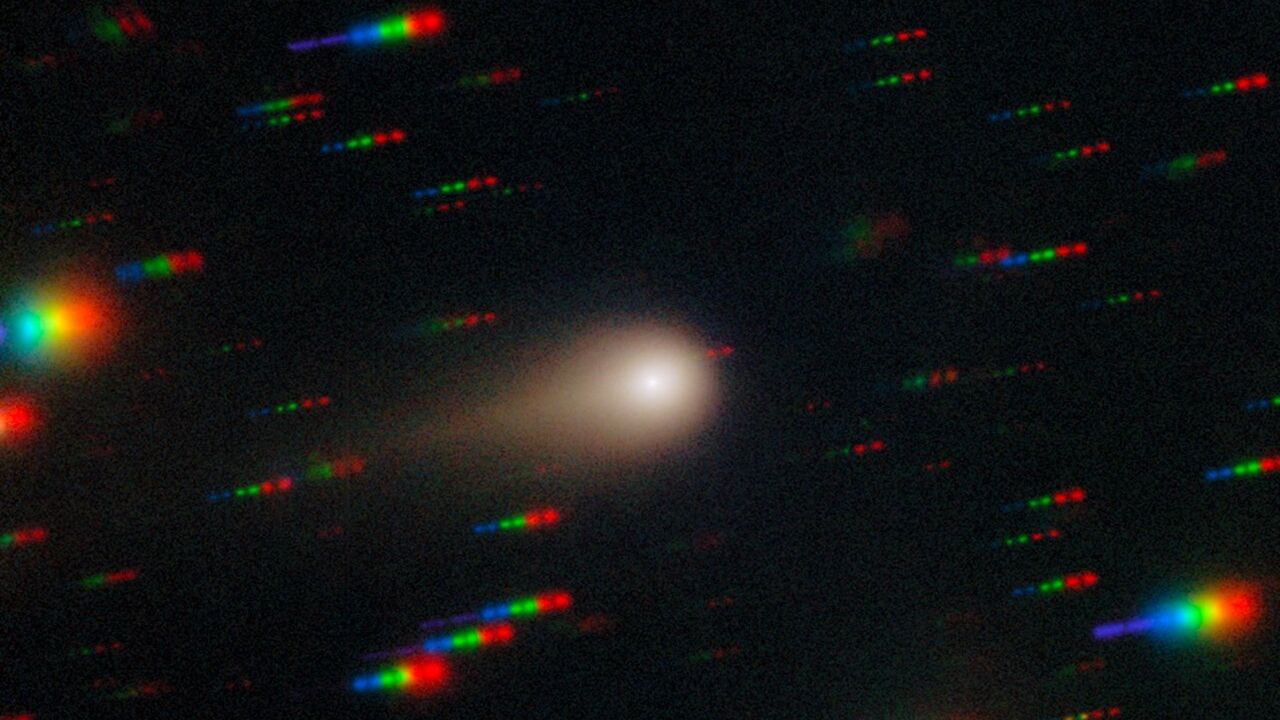

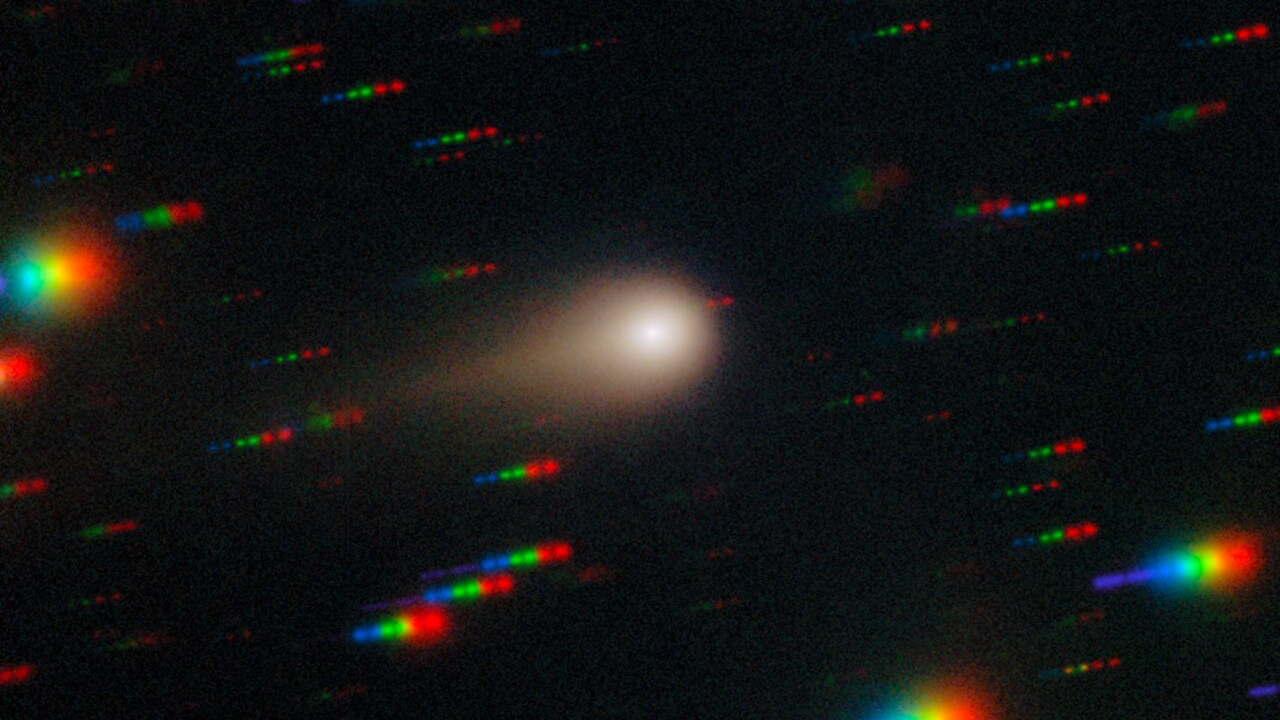
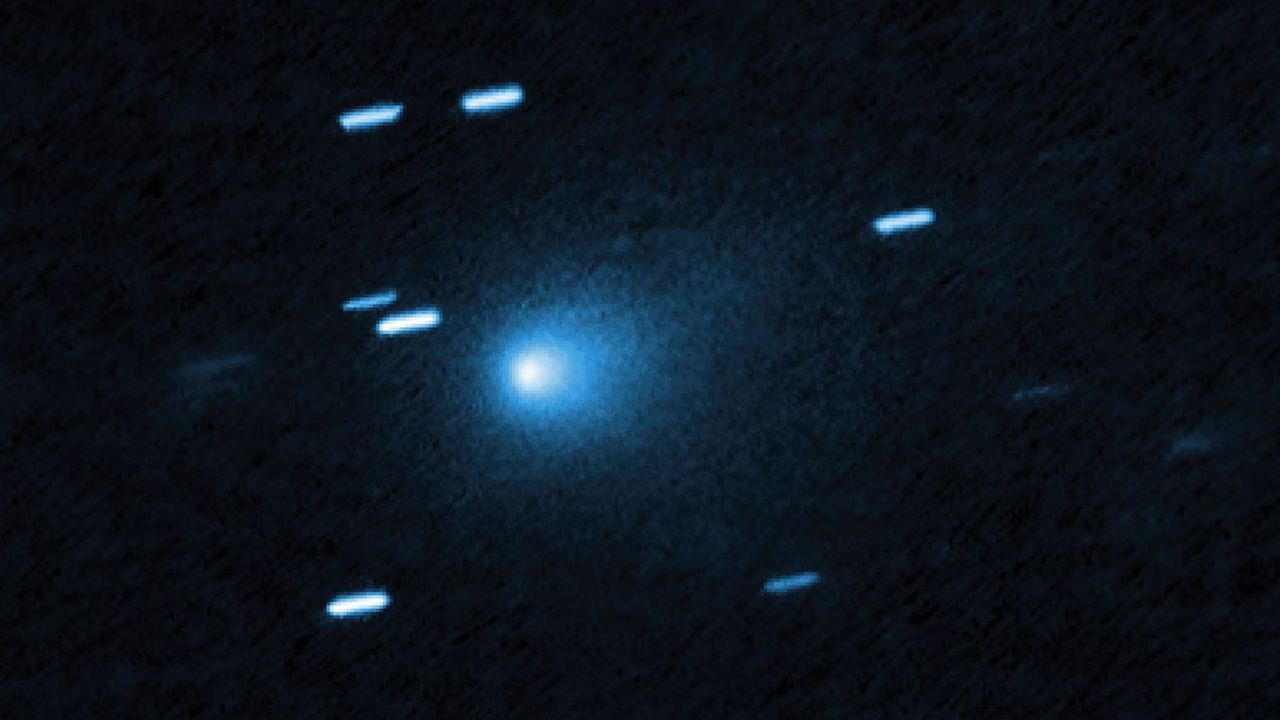
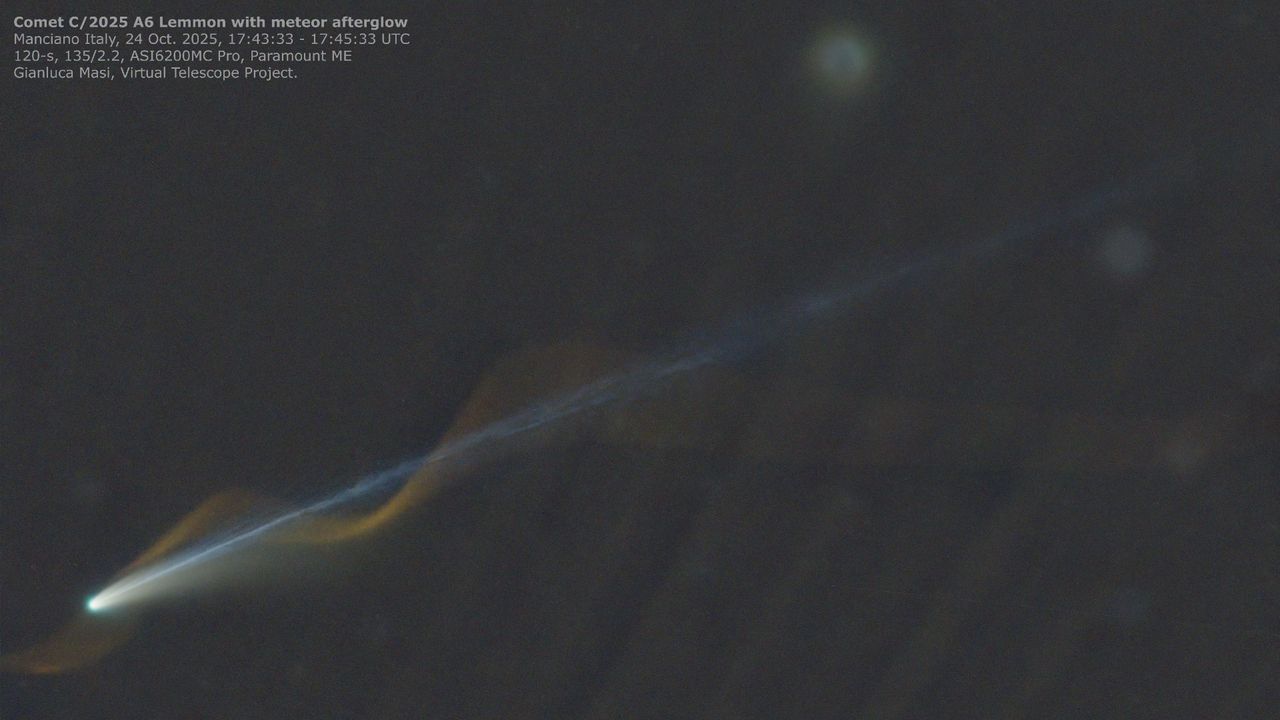
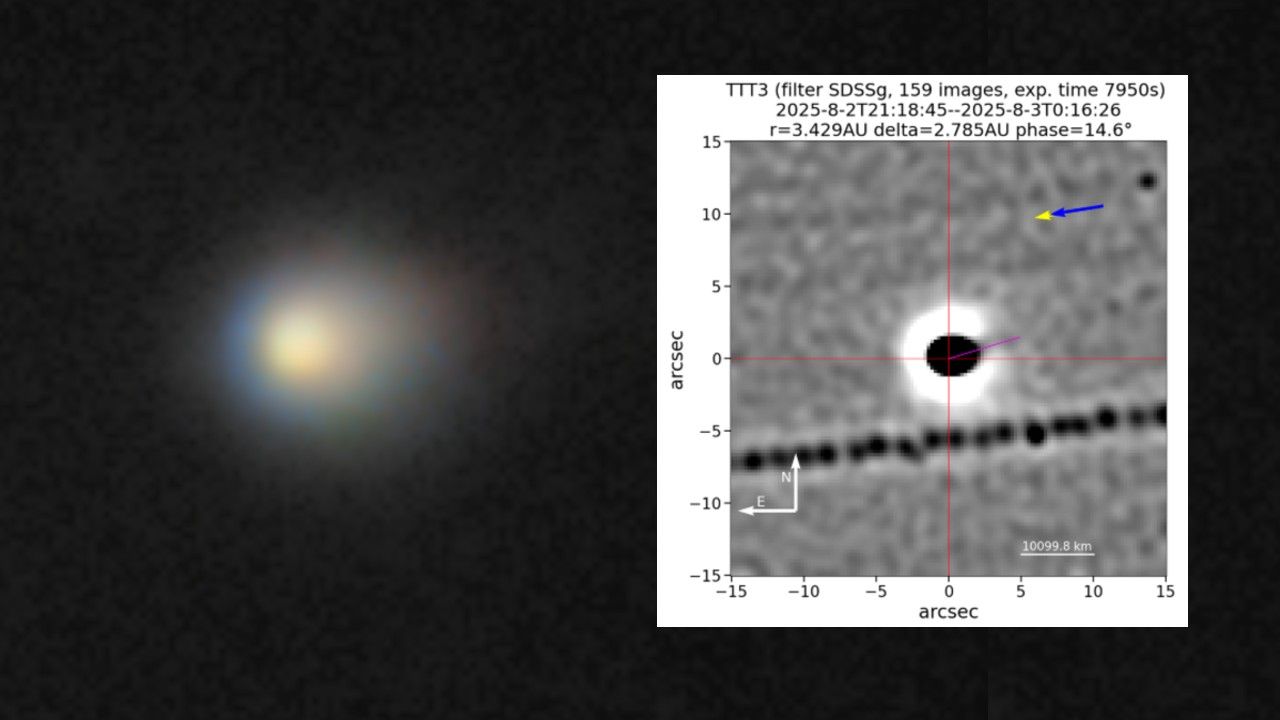
The interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS is approaching its closest point to the sun, known as perihelion, which will occur on October 29. This event is significant as it raises questions about how the comet will appear when it reemerges on the other side of the sun. Observing its changes can provide valuable insights into the behavior of interstellar objects and enhance our understanding of the cosmos.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System