Uranus and Neptune may not be 'ice giants' after all, new research suggests
NeutralScience
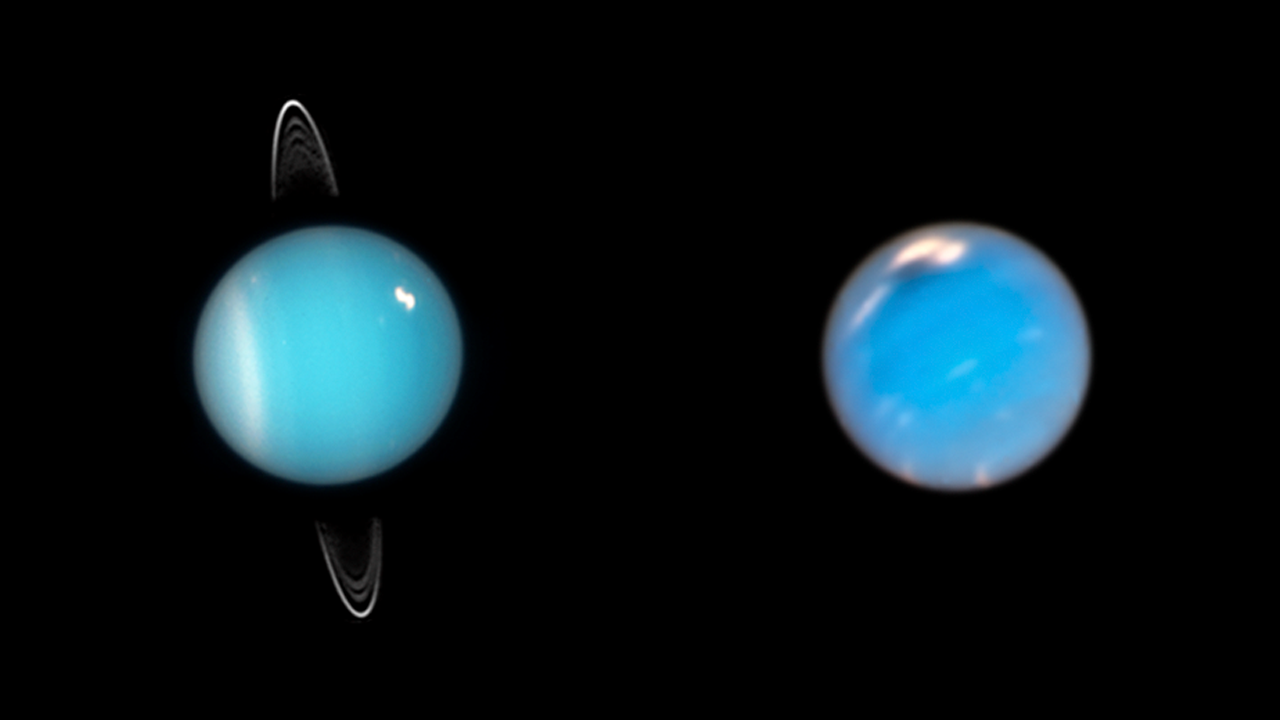

New research suggests that Uranus and Neptune, traditionally classified as 'ice giants', may be better described as 'rocky giants'. This revelation stems from our limited understanding of the internal structures of these distant planets. By re-evaluating their composition, scientists hope to gain deeper insights into their formation and evolution, which could reshape our knowledge of planetary science.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System