See a razor-thin crescent moon line up with Mars and Mercury at sunset on Oct. 23
PositiveScience
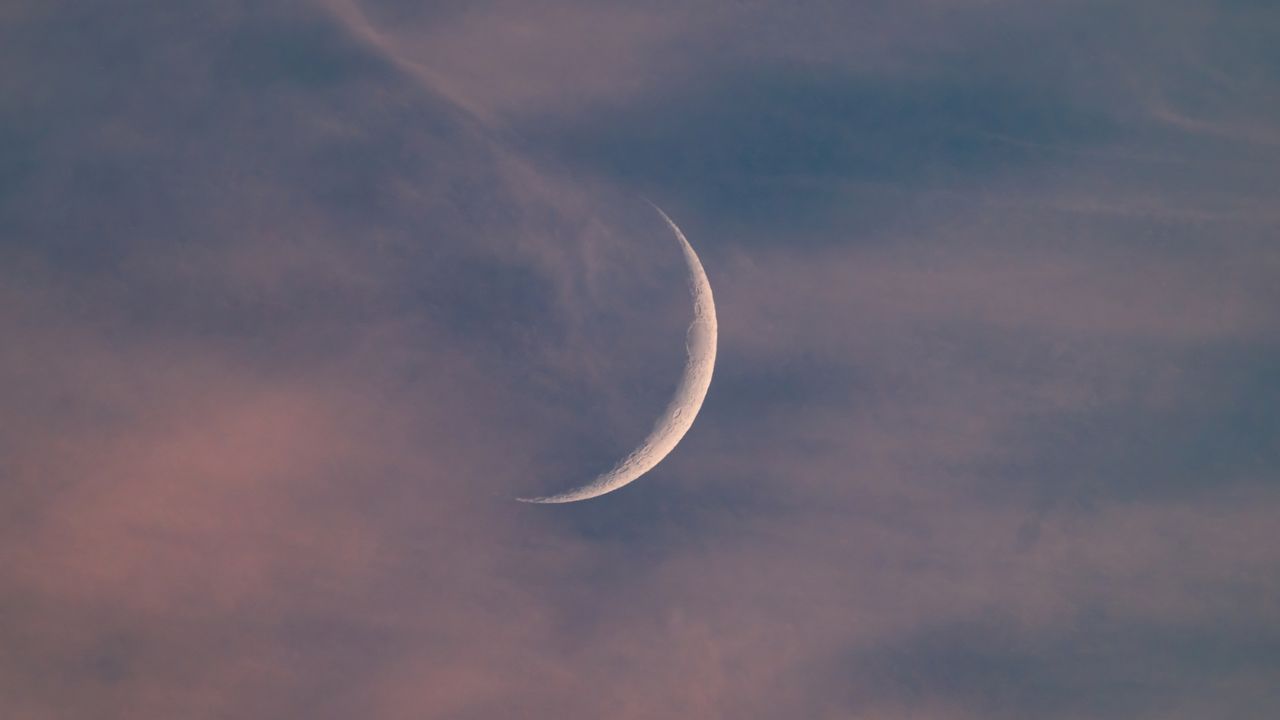

On October 23, skywatchers will be treated to a stunning sight as a thin crescent moon aligns with Mars and Mercury at sunset. This celestial event is not just a beautiful spectacle; it offers a unique opportunity for astronomy enthusiasts and casual observers alike to appreciate the wonders of our solar system. Such alignments remind us of the intricate dance of celestial bodies and encourage people to look up and connect with the universe.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System