Astronomers may have glimpsed evidence of the biggest stars ever seen
PositiveScience

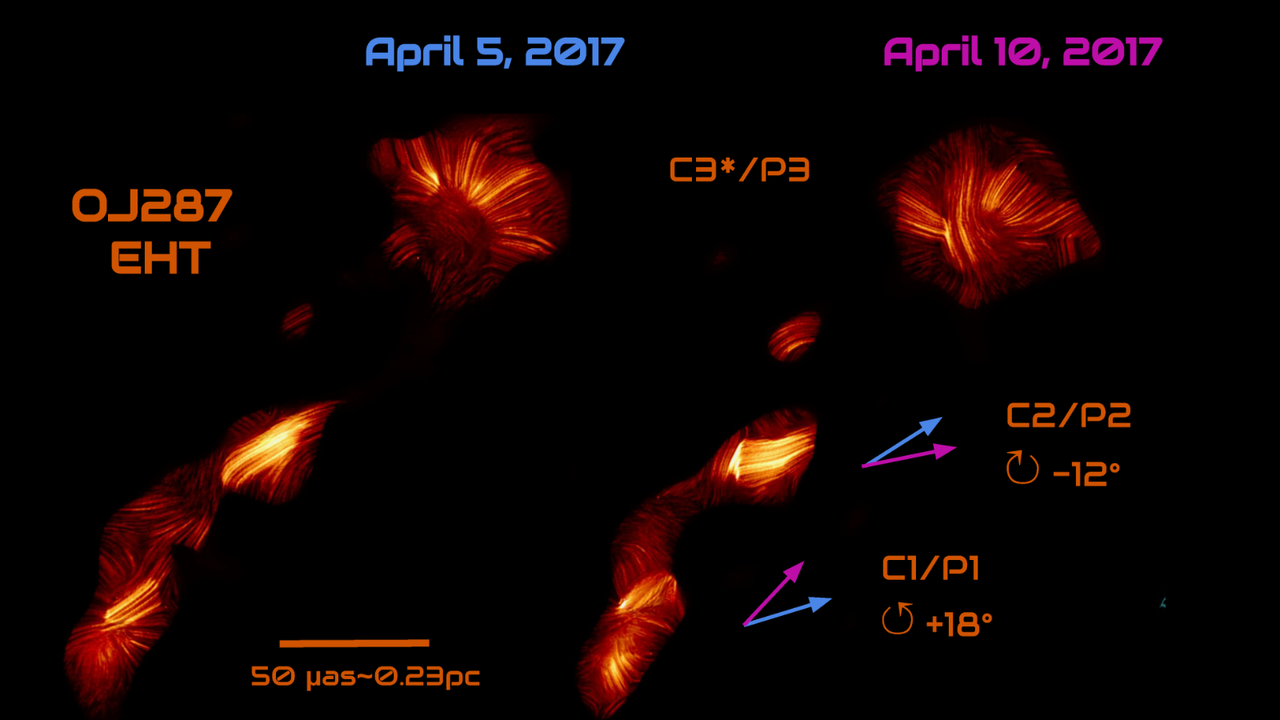
- Astronomers may have glimpsed evidence of supermassive stars, which could range from 1,000 to 10,000 solar masses, potentially solving mysteries surrounding the formation of large black holes.
- This finding is crucial as it could reshape current understanding of black hole evolution and their relationship with massive stars in the universe.
- The discovery aligns with recent observations of black hole flares and eruptions, highlighting the dynamic interactions between stars and black holes, and emphasizing the ongoing exploration of cosmic phenomena.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System