Wildfire smoke lofted miles high could have an unexpected effect on Earth's climate
NeutralScience
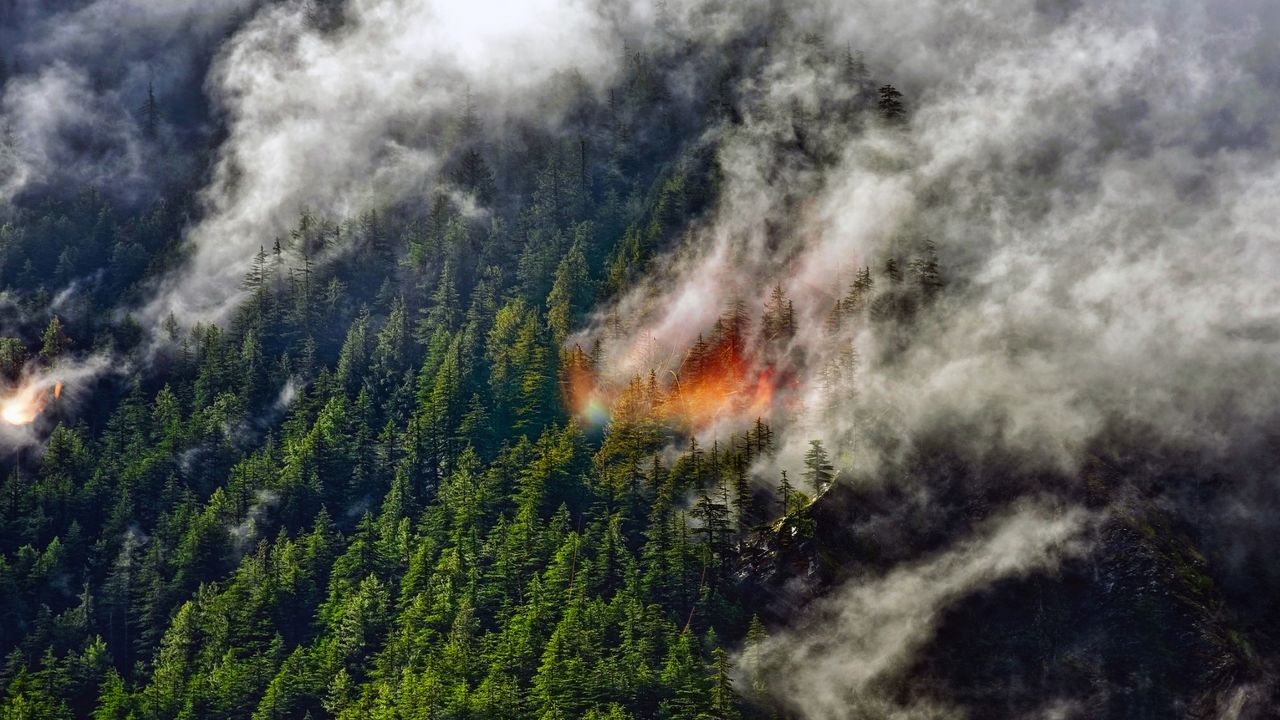

- New measurements indicate that smoke particles from wildfires, when lofted miles high into the atmosphere, are twice the size of those found at lower altitudes. This finding highlights a significant difference in the behavior of smoke particles depending on their altitude.
- The implications of this discovery are critical for understanding the effects of wildfire smoke on Earth's climate. Larger smoke particles may influence atmospheric processes and climate patterns in ways that were previously underestimated, potentially affecting weather and air quality on a global scale.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System