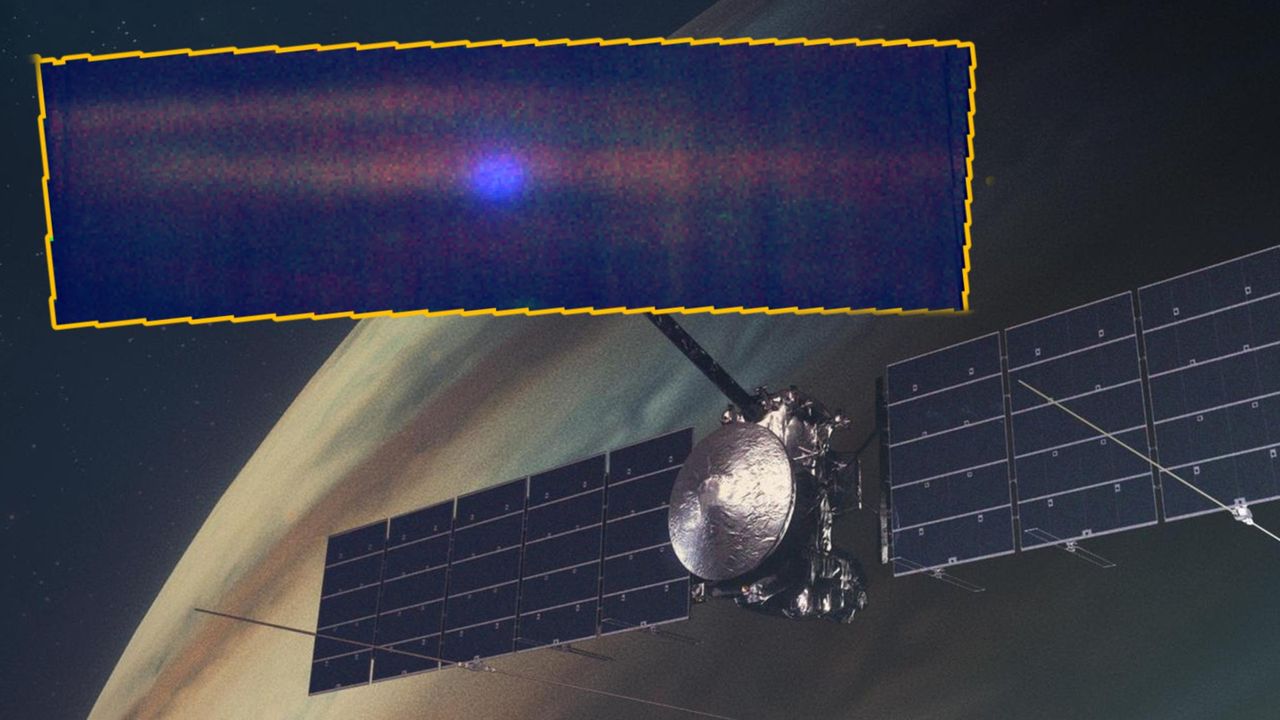
Scientists detect X-ray glow from interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS extending 250,000 miles into space
PositiveScience
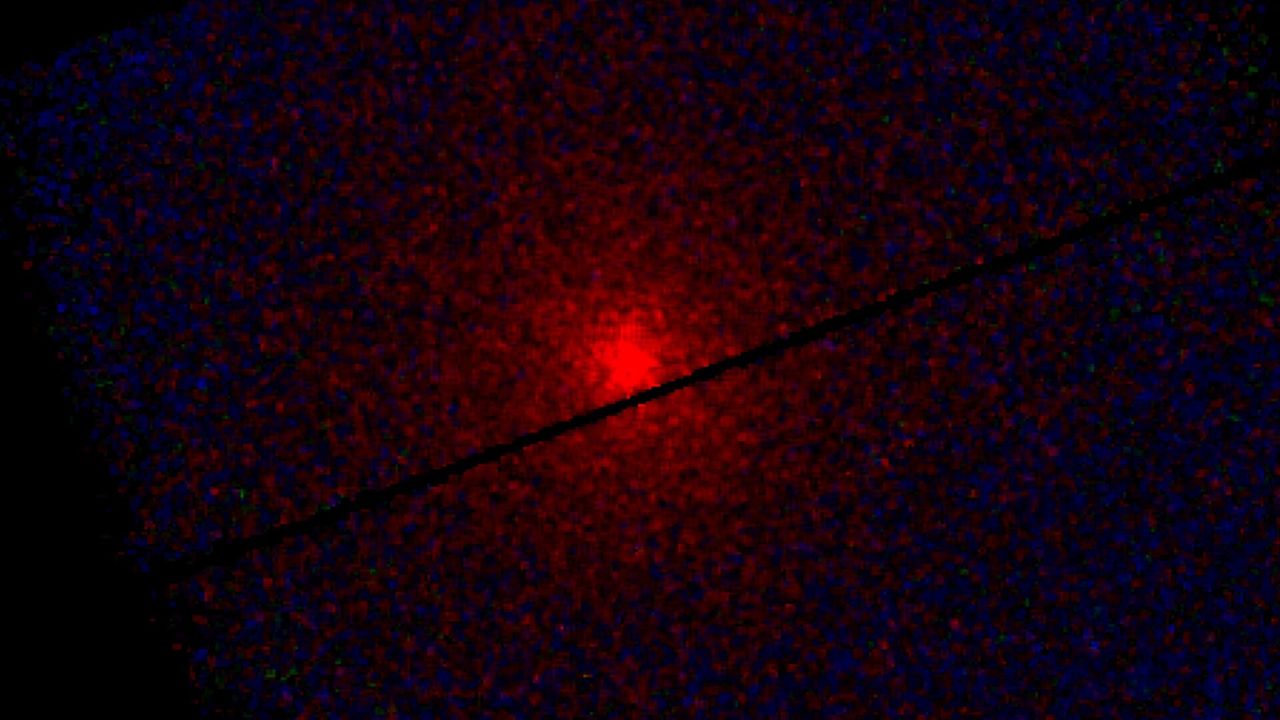

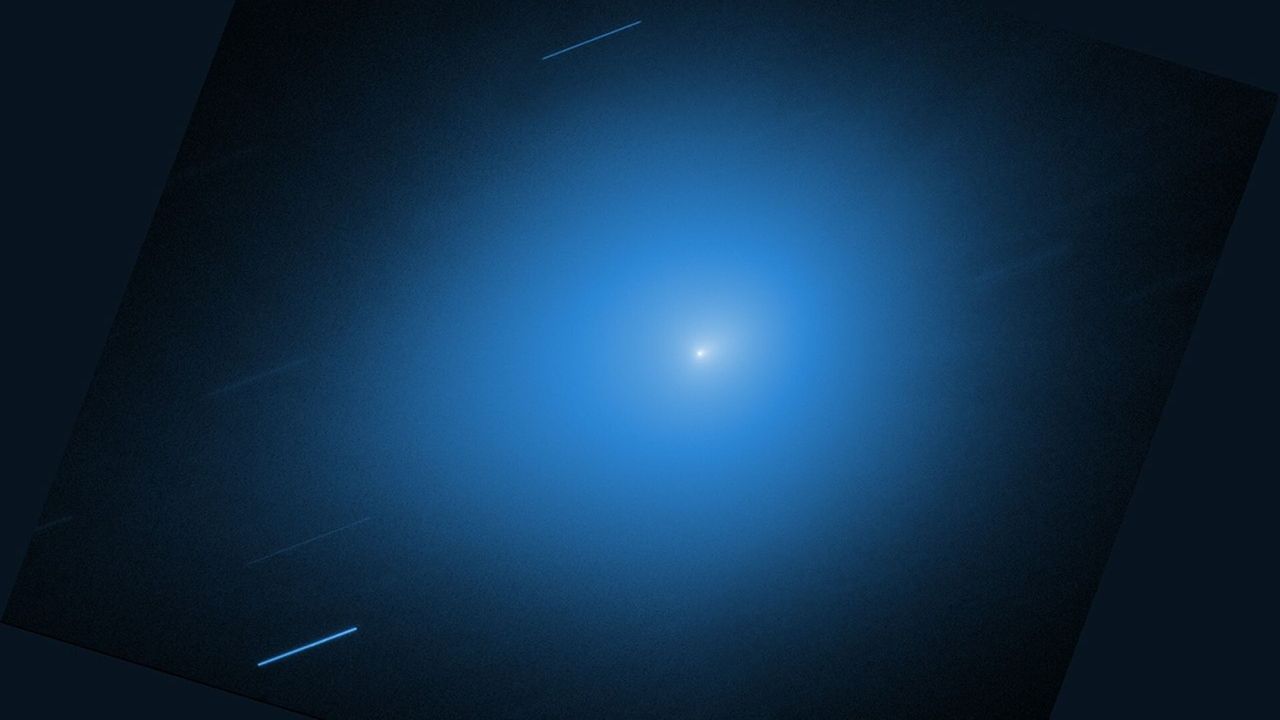
- Scientists have detected an X-ray glow from the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, which extends approximately 250,000 miles into space. This observation was made using two space telescopes, revealing how the comet's gases interact with solar particles as it traverses the inner solar system.
- This discovery is significant as it enhances the understanding of the comet's composition and behavior, providing insights into the interactions between interstellar objects and solar radiation, which is crucial for future astronomical studies.
- The ongoing observations of 3I/ATLAS, including its recent close flyby of Mars and the detection of cryovolcanoes, underscore the comet's dynamic nature and its importance in studying the characteristics of interstellar bodies, contributing to broader discussions about the origins and evolution of such celestial phenomena.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System