AI helps build the most detailed Milky Way simulation ever, mapping 100 billion stars
PositiveScience
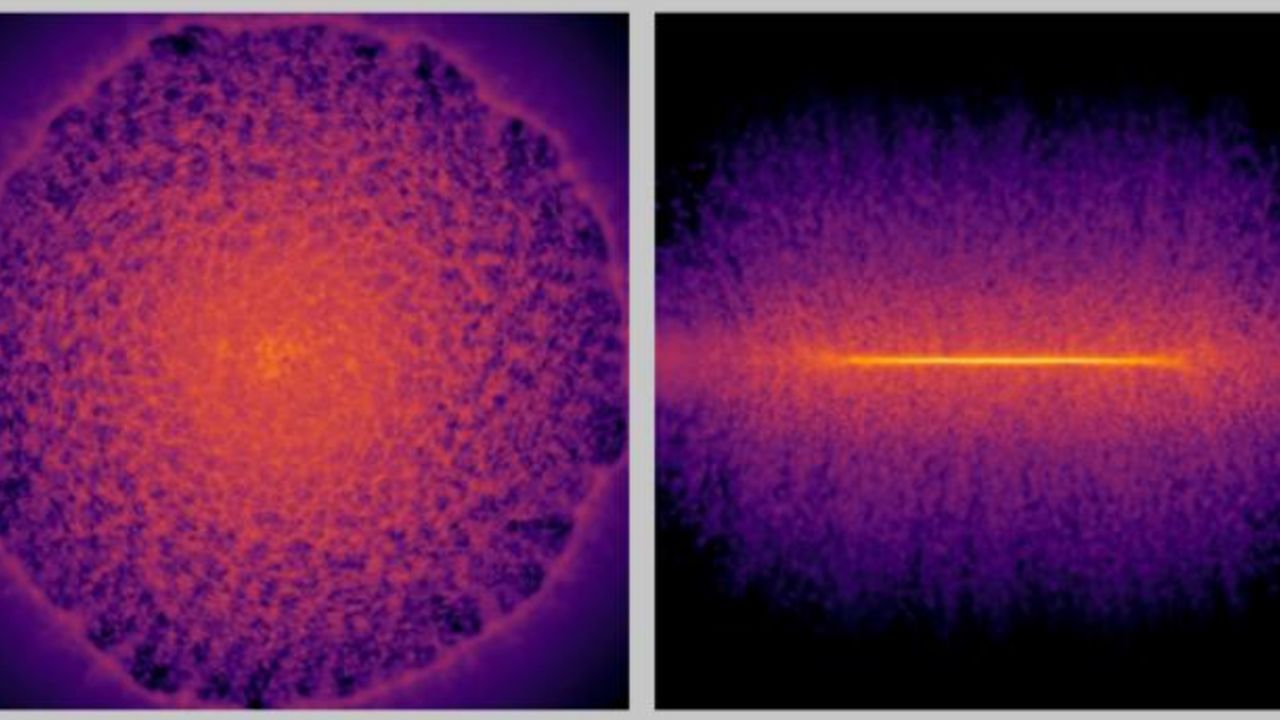
- A new simulation model has mapped 100 billion stars in the Milky Way, marking a significant advancement in astronomical research. This model allows for faster processing and the inclusion of smaller events like supernovae in the simulation.
- This development is crucial as it enhances our understanding of the Milky Way's structure and dynamics, potentially leading to new discoveries in astrophysics and improving the accuracy of future simulations.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System