How Mars' ancient lakes grew shields of ice to stay warm as the Red Planet froze
NeutralScience
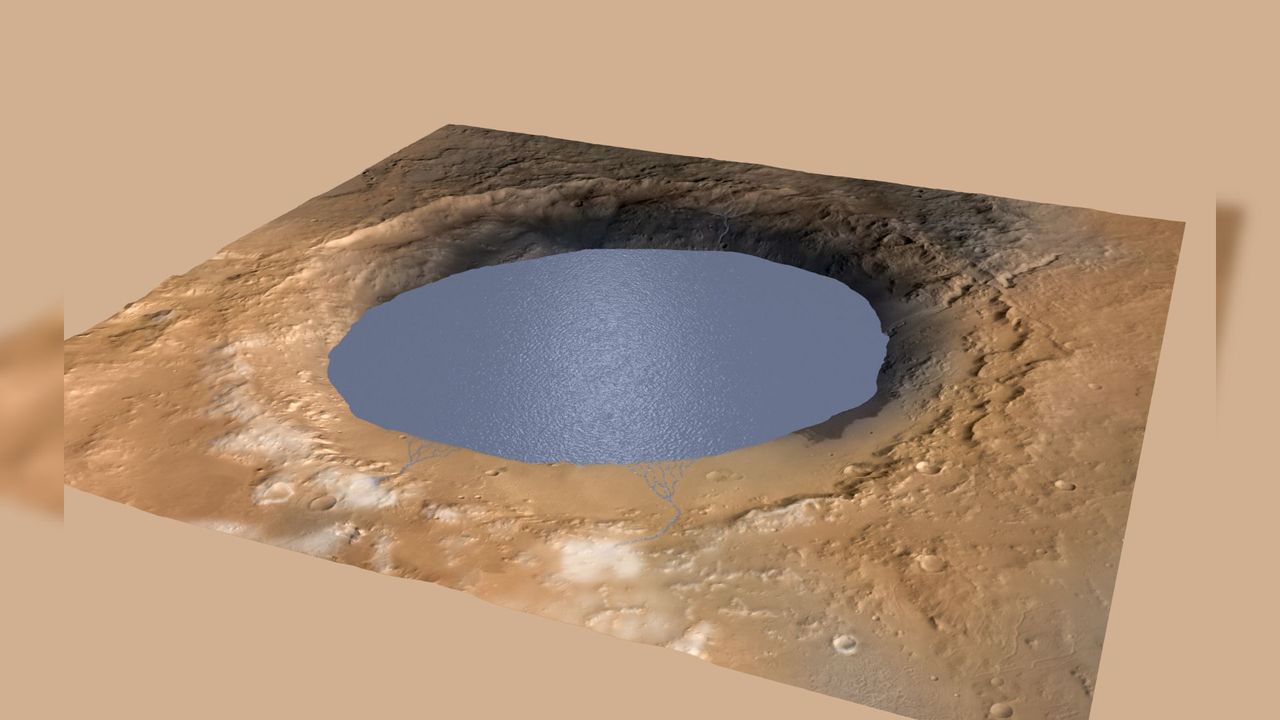
- Recent findings suggest that ancient lakes on Mars developed ice shields to maintain warmth, potentially explaining how liquid water persisted on the planet despite a colder climate. This discovery sheds light on Mars' hydrological history and its capacity to support water in various forms.
- Understanding the mechanisms that allowed liquid water to exist on Mars is crucial for comprehending the planet's past climate and its potential for hosting life. This knowledge could inform future exploration and the search for extraterrestrial life.
- The presence of ice and water on Mars ties into broader discussions about the planet's geological history, including the implications of lightning activity, ancient water traces in unique surface features, and the potential for human survival using Martian ice as a resource.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System