Geminids 2025: The year's best meteor shower is coming, with a second shower hot on its tail
PositiveScience

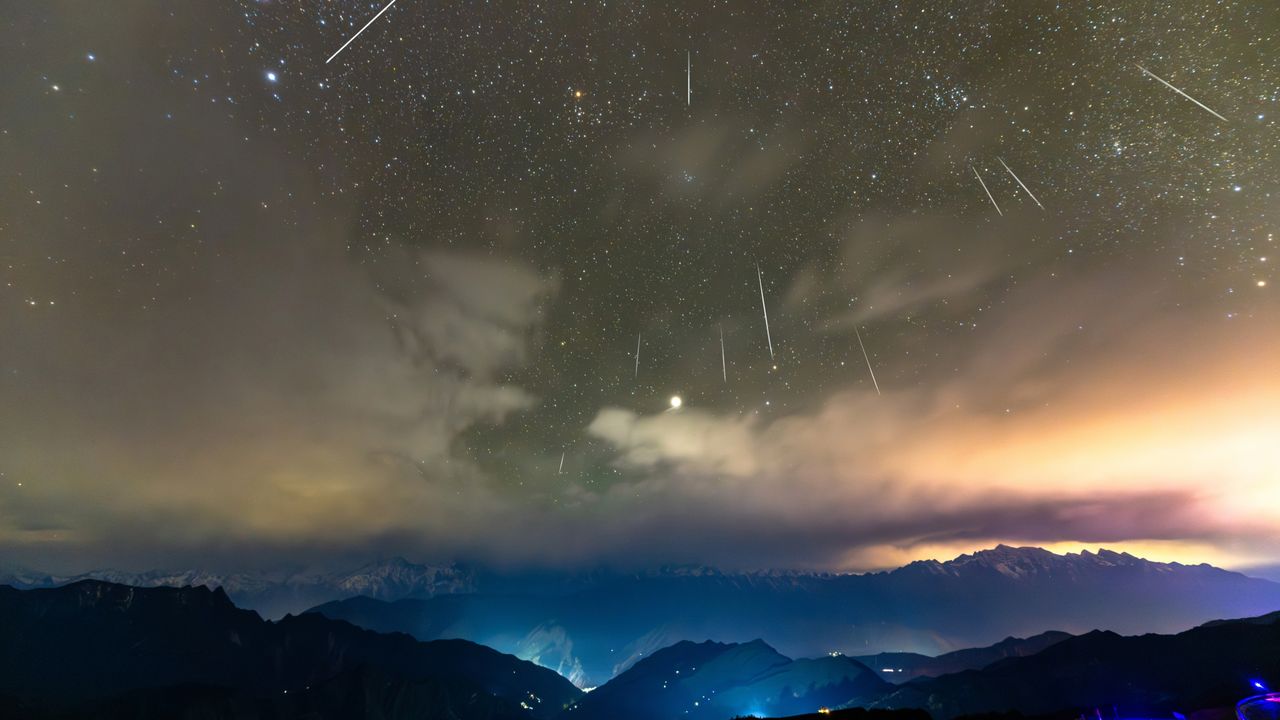
- The Geminid meteor shower has commenced, with its peak expected on the nights of December 13 and 14, 2025, offering a spectacular display of up to 150 shooting stars per hour in a moonless sky. This annual event is renowned for its vibrant and colorful meteors, captivating stargazers around the world.
- The significance of the Geminid meteor shower lies in its status as one of the most anticipated celestial events of the year, drawing attention from both amateur and professional astronomers. Its occurrence provides a unique opportunity for public engagement with astronomy and enhances appreciation for natural phenomena.
- This meteor shower not only highlights the beauty of the night sky but also serves as a reminder of the ongoing interest in celestial events. As one of the most prolific meteor showers, the Geminids contribute to a broader understanding of meteor activity and the dynamics of our solar system, fostering a sense of wonder and curiosity about the universe.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/62/01/62019da1-dd28-4322-aca0-0ec598b63235/7402439760_6437bcb924_k.jpg)