Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS shines in new image captured after close pass by the sun (photo)
PositiveScience
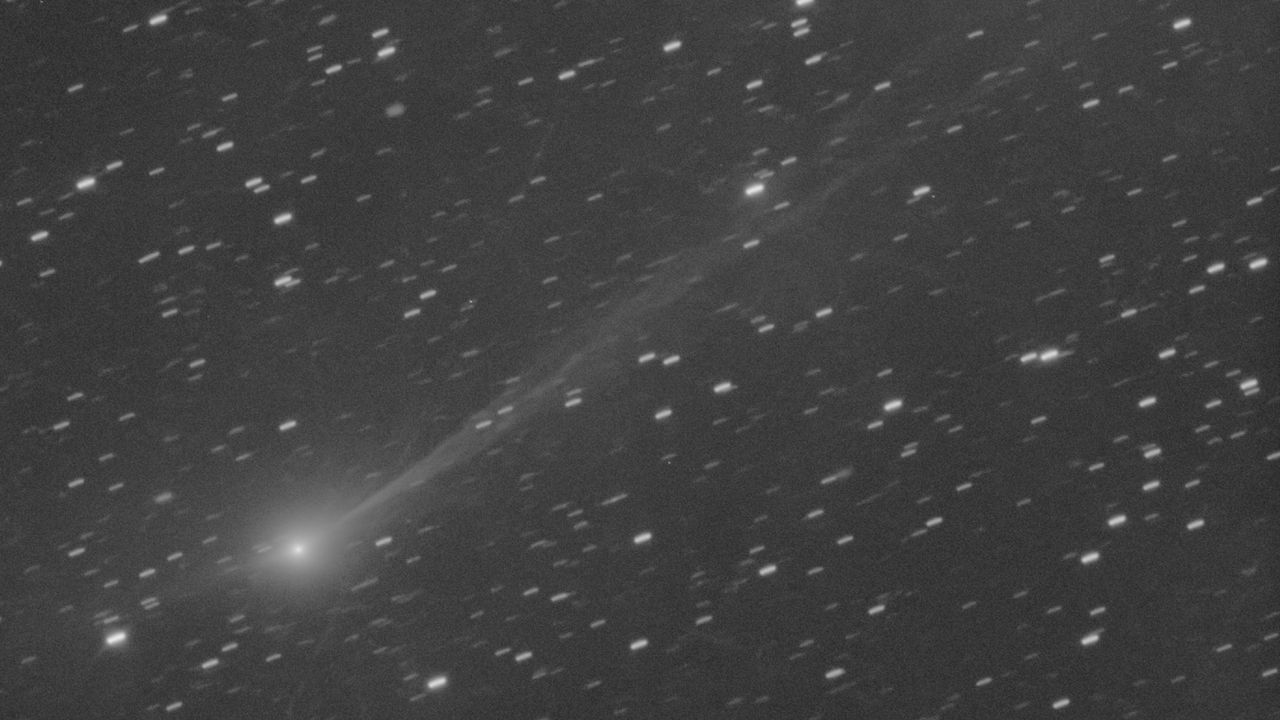

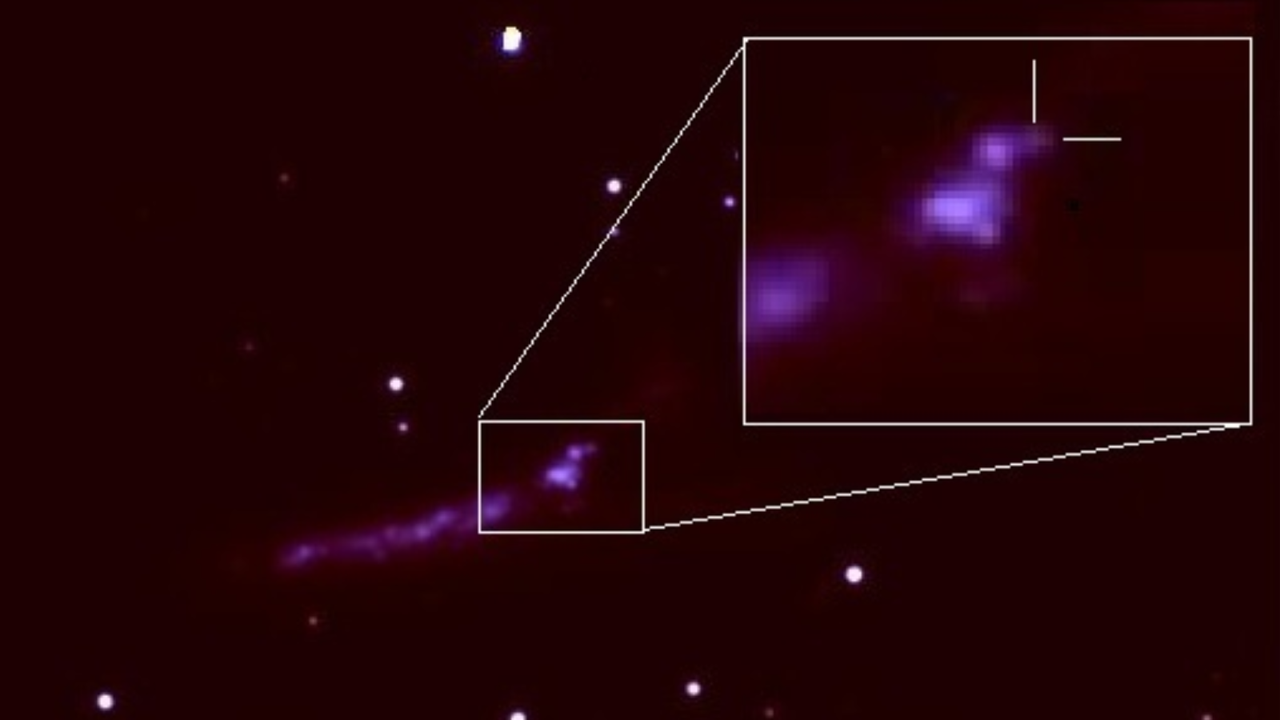
- The interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS has been photographed after its close pass by the sun, revealing its evolution and unique features. This image highlights the comet's interstellar origins and its behavior as it interacts with solar radiation.
- The observation of 3I/ATLAS is significant as it enhances understanding of interstellar objects and their dynamics, contributing to the broader field of astronomy and the study of celestial bodies.
- This event underscores the ongoing interest in comets, particularly those from beyond our solar system, as they provide critical data on the formation and evolution of celestial phenomena.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System