A fossilized foot found 15 years ago belonged to enigmatic human relative that lived alongside Lucy, scientists say
PositiveScience
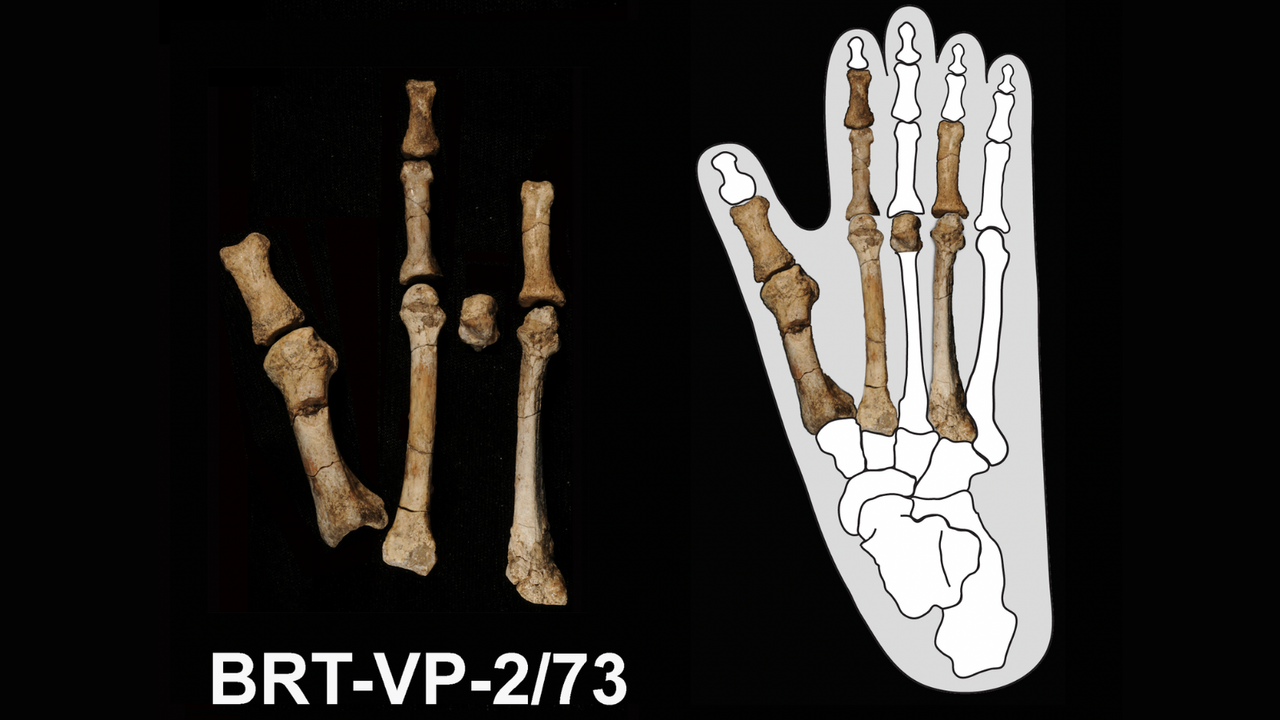
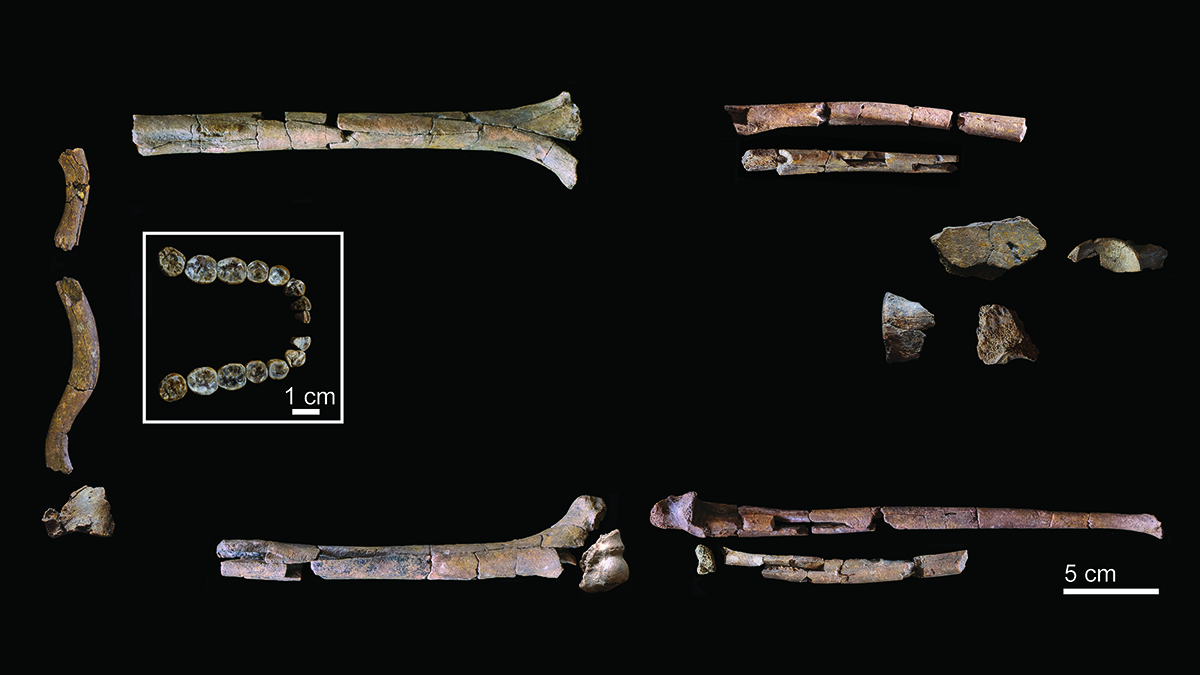
- Scientists have announced that a fossilized foot discovered 15 years ago belonged to a previously unknown human relative that lived alongside the famous fossil known as Lucy. This finding, along with recently unearthed jaw bones and teeth, indicates that early human relatives experimented with various walking strategies before settling on a specific method.
- This discovery is significant as it enhances the understanding of human evolution, particularly the diversity of locomotion among early hominins. It suggests that multiple species coexisted and adapted in different ways, contributing to the evolutionary narrative.
- The implications of this research extend to the broader understanding of human ancestry, as it highlights the complexity of evolutionary paths taken by early hominins. The findings resonate with ongoing discussions about the timeline of human evolution and the adaptations that shaped our species, particularly in light of other recent discoveries that challenge previous assumptions about when and how human evolution occurred.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System






