NASA discovers 'space gum' and sugars 'crucial to life' in asteroid Bennu samples brought to Earth (video)
PositiveScience
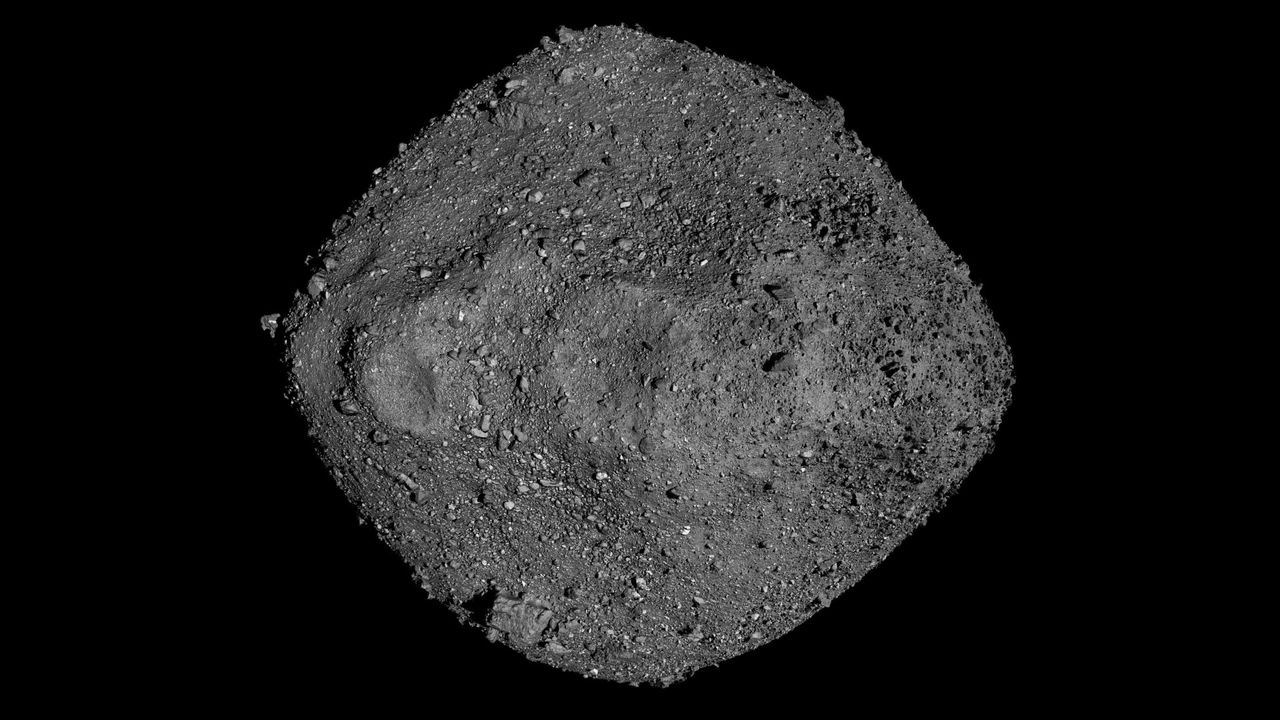

- NASA has announced the discovery of life-friendly sugars and a peculiar substance referred to as 'space gum' in samples collected from the asteroid Bennu. These findings, which also include ancient stardust, were brought back to Earth for analysis, highlighting the potential for organic compounds in space environments.
- This development is significant as it enhances understanding of the building blocks of life and suggests that asteroids like Bennu may have played a crucial role in delivering essential materials to early Earth, potentially influencing the origins of life.
— via World Pulse Now AI Editorial System